Essential Compound Movements
First and foremost, you must induce your kind; an injury sustained during coaching can impair your performance and motivation.
The three main compound training you should understand are:
- Squat
- Deadlift
- Bench Press
Compound movements are a great exercise to focus on the muscle throughout the skeleton because they stress a lot of muscle teams, which then causes the androgenic hormone to be discharged into the bloodstream, which is quickly followed by processes that help gain muscle and get stronger.
Other effective compound training
- Bent over rolls
- Military press
- Dips (weight or not weight)
- cleans
- Pull-ups
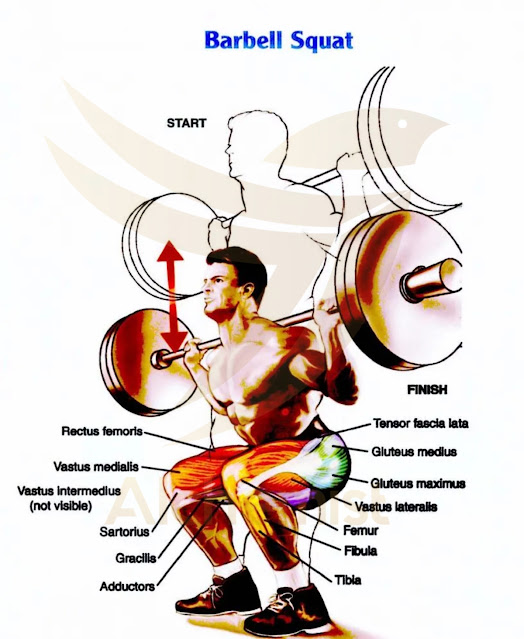
SQUAT
The squat may be a multi-joint practice to realize muscle mass and a few severe strengths because it targets a range of muscle teams throughout the body.
This training is primarily for your legs; it puts a lot of strain on the hamstrings, quads, and thus the gluteus muscle.
The gluteus maximus is the largest gluteus muscle group; it works with the hamstrings to help with hip extension.
Throughout squats, the gluteal muscle is most long (eccentric contraction) to manage the speed of the downward movement of the squat; conversely, the muscle shortens (concentric contraction), followed by the knee and hip extension within the upward movement part of the squat.
Hamstrings are an area unit created from three muscles: the skeletal muscle of the leg bone, the semimembranosus, and the semitendinosus.
Hamstrings are being worked after you squat; it helps the gluteus muscle with hip extension. Hamstrings lengthen throughout the downward movement of the squat and shorten throughout the upward trend of the squat.
A quadriceps is a muscle group of four muscles: the vast lateral, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius.
The quads are involved in most knee extensions; they lengthen (eccentric contraction) during the squat's downward movement and shorten during the squat's upward trend.
The squat additionally puts work on the lower back muscle cluster; the muscles on your lower back contract isometrically ( Joint angle and muscle length don't modify throughout contraction) throughout each downward movement and upward movement of the squat.
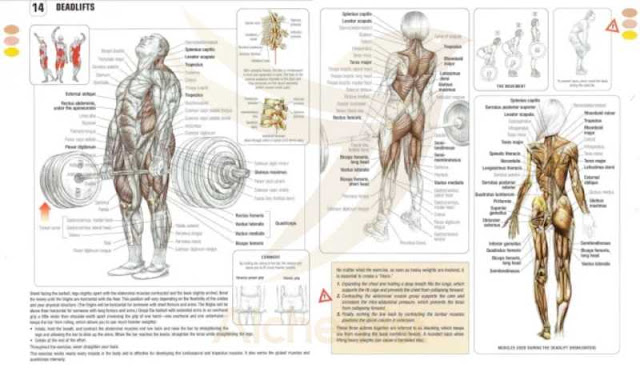
DEADLIFT
The deadlift is one of the most rigorous exercises because it helps build muscle and strength, which is why many powerlifters use it as one of the three lifts used in powerlifting.
The deadlift targets several muscle teams; the primary muscles used are the erector spinae, gluteus maximus, quadriceps, hamstring, and therefore the adductors.
It's extremely advanced and time-consuming to clarify all the muscles' contractions throughout the elevate; therefore, for additional interest in any detail of the muscles' contractions, please review the muscle anatomy below.
How to deadlift properly
BENCH PRESS
The bench press consists of delivering the weighted barbell downward during a controlled motion to the chest and then pushing the bar
In scientific terms, the muscle teams around the shoulder area are accustomed to horizontal abduction. The bench press focuses on the chest, shoulders, and skeletal muscles.
Other muscle teams are targeted with bench pressing; for details, look into the muscle anatomy for the bench press.
Pectorals (Chest)
The pectoralis major and minor muscles, located below the key, form the chest. Within the downward movement part of the bench press, chest muscles bear eccentric contraction (lengthen) and consent to the upward movement part of the press (shorten).
Shoulder Muscles
Bench presses primarily target the anterior deltoids, which are made up of several muscle teams.
The anterior deltoids bear eccentric contraction (lengthening) throughout the downward part of the bench press; they contract concentrically throughout the upward part of the bench press.
Throughout the downward part of the bench press, the skeletal muscles contract eccentrically (lengthen).
Therefore, they shorten throughout the upward part of the bench press, wherever they bear homocentric contraction.
It's a vital element of the bench press; it emphasizes your skeletal muscle heavily, so having strong skeletal muscle can boost your bench press.
Nutrient necessities (Basic)
Make sure that you:
- Eating a great amount of food containing advanced carbohydrates, e.g., rice (preferably brown rice) and other foods
- foods high in sodium, such as chicken and beef
- Good fats, e.g., avocado and almond (for that omega-6)
- Get your minerals, vitamins, and fiber
- Drink a sensible quantity of water; a pair of cubic meters would be nice